Logging
OpenTwin provides a Logger Service that can receive log messages from multiple services. The Logger Service stores the received log messages and forwards them to any registered Log Receiver.
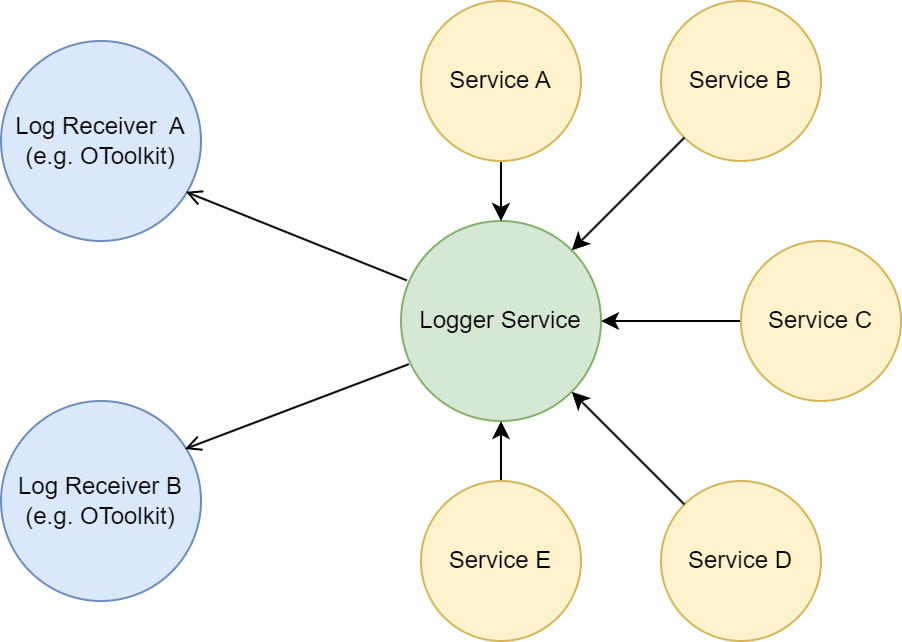
Setup Logger
If the central logging system (using the Logging service) is required then the OTCommunication/ServiceLogNotifier should be used.
The initialize method ot the ServiceLogNotifier will call the initialize method of the LogDispatcher and register the ServiceLogNotifier object at the LogDispatcher.
#include "OTCommunication/ServiceLogNotifier.h"
char * init(const char * _arg1, const char * _arg2, const char * _arg3, const char * _arg4) {
#ifdef _DEBUG
// In a Debug configuration the log messages should also be written to std::cout (true).
ot::ServiceLogNotifier::initialize("MyServiceName", "LoggingServiceURL", true);
#else
// In a Release configuration the log messages should not be written to std::cout (false).
ot::ServiceLogNotifier::initialize("MyServiceName", "LoggingServiceURL", false);
#endif
...
}
Note
If the service is using the OTServiceFoundation/Foundation the ot::foundation::init method will call ot::ServiceLogNotifier::initialize by providing the service name that is set in the provided ApplicationBase object.
When creating the ServiceLogNotifier instance, it sets the logging options from the environment variables.
Note
The environment variables are optional. When launching OpenTwin via the batch files provided with OpenTwin the variables will be set if not done so in the system/user environment.
Environment variables
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
OPEN_TWIN_LOGGING_URL |
The URL where the Logger Service is running at. If the URL is either empty, or starts with |
OPEN_TWIN_LOGGING_MODE |
Sets the active log flags that determine which log messages will be generated. A union of multiple flags can be created by splitting them with a ‘|’ character without any blank spaces (e.g.
|
OPEN_TWIN_LOG_BUFFER_ROOT |
If set, logs will be written to files at this directory by the logger service. |
OPEN_TWIN_LOG_BUFFER_SIZE |
The buffer size in bytes used for the log buffer files (default is 200MB) Requires OPEN_TWIN_LOG_BUFFER_ROOT to be set. |
OPEN_TWIN_LOG_BUFFER_FILECOUNT |
Number of files used by the logger service file buffer (default is 3). Requires OPEN_TWIN_LOG_BUFFER_ROOT to be set. |
OPEN_TWIN_FILE_LOGGING |
If set to true file logging will be enabled. |
Generate Log Messages
To generate log messages at any point in your code use the macros defined in the OTCore/Logger.h header file.
Log messages will be send to the Logger Service if the provided log flags are allowed.
#include "OTCore/Logger.h"
namespace test {
void foo(void) {
OT_LOG_I("Hello World!");
}
}
The example above will generate a log message with:
Service name: The service that was set in the initialize function.
Function name: test::foo.
Type: Information.
Text: Hello World!.
LocalSystemTime: The time where the Log message object was generated (UTC).
GlobalSystemTime: The time when the Log message was received by the LoggerService (UTC).
Log Macros
OT_LOG_IInformation log: General information.OT_LOG_DDetailed log: Detailed information.OT_LOG_WWarning log.OT_LOG_EError log.OT_LOG_TTest log.
If any other log type(s) should be set for the log message, use the OT_LOG macro and provide the desired flags.
The Information, Detailed, Warning, Error and Test log macros have the following special types:
AAssert before log. The log message will be displayed in the assert messsage. Message must be a C-String (const char*) (e.g. LOG_EA(“Test”) -> Log Error & Assert).ASAssert simple before log. The Assert will have no message set. Especially useful when wanting to assert but to log a std::string at the same time (e.g. LOG_EAS(“Test: “ + myString) -> Log Error & Assert simple).
Use file logging
If the log messages should be written to a file the environment variable OPEN_TWIN_FILE_LOGGING should be set to true.
If the file logging is enabled all log messages will be written to a file in the working directory of the application.
The file name is <Service Name>.otlog.
Note
A valid service name must be provided to the ot::LogDispatcher::initialize or ot::ServiceLogNotifier::initialize method.
View the Log
There are two approaches to view the log messages.
The first one is to register a receiver at the logger service, this receiver will get all the currently buffered log messages when registrating at the Logger Service. Afther the registration the receiver will receive a copy of every new log message.
The second approach is to request the currently buffered log messages.